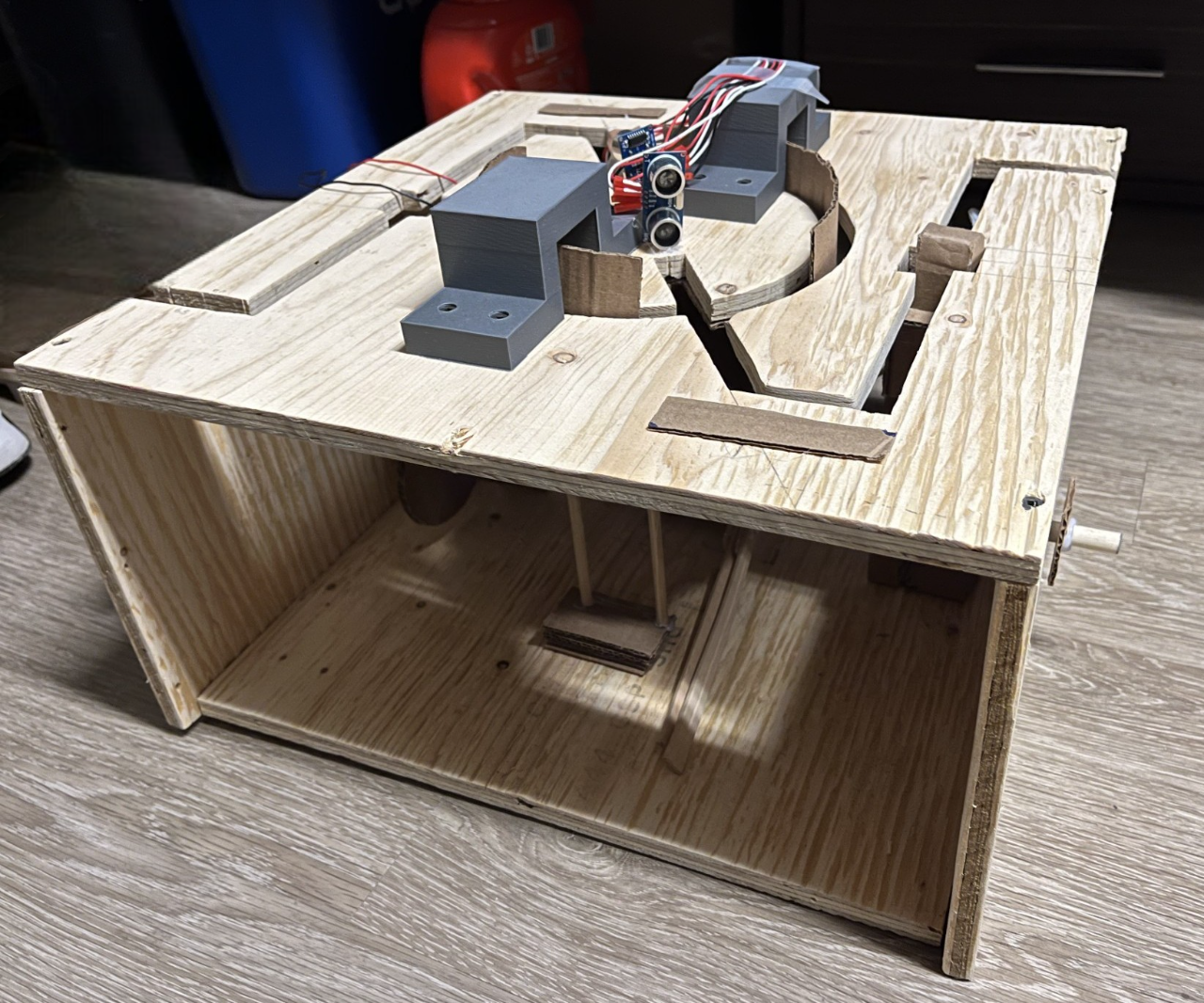
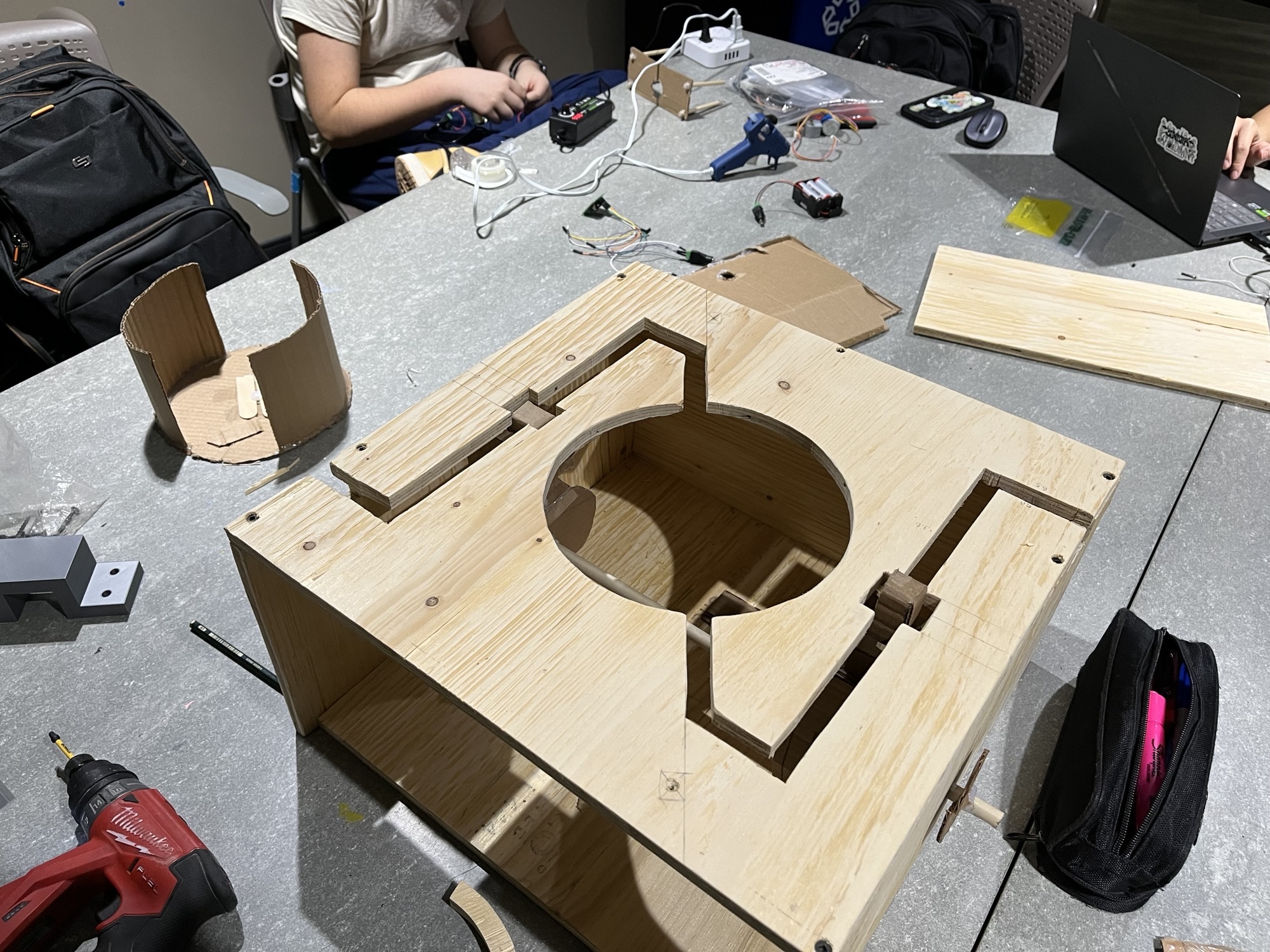
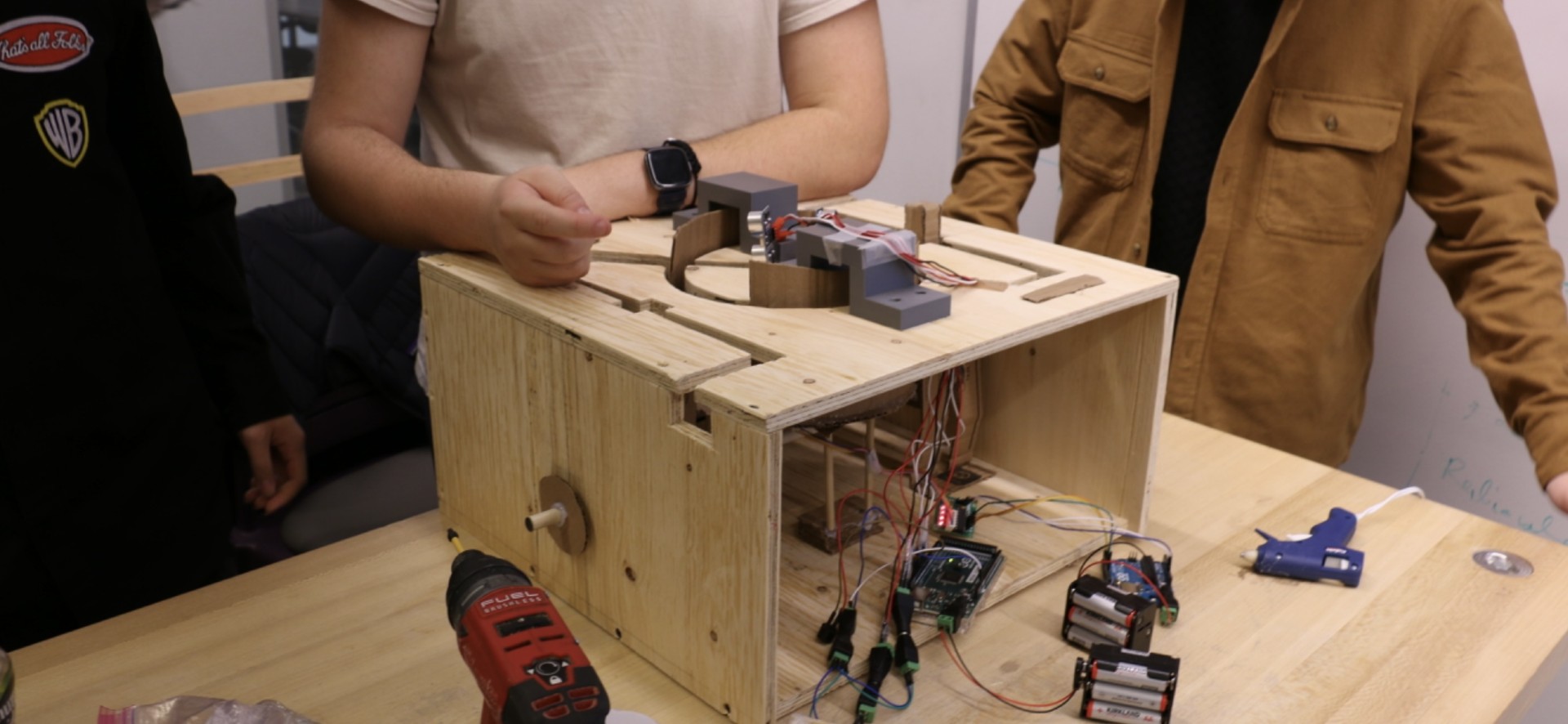
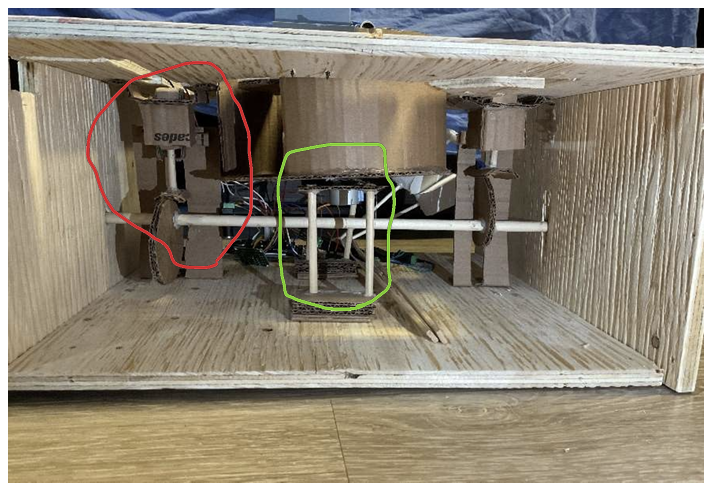
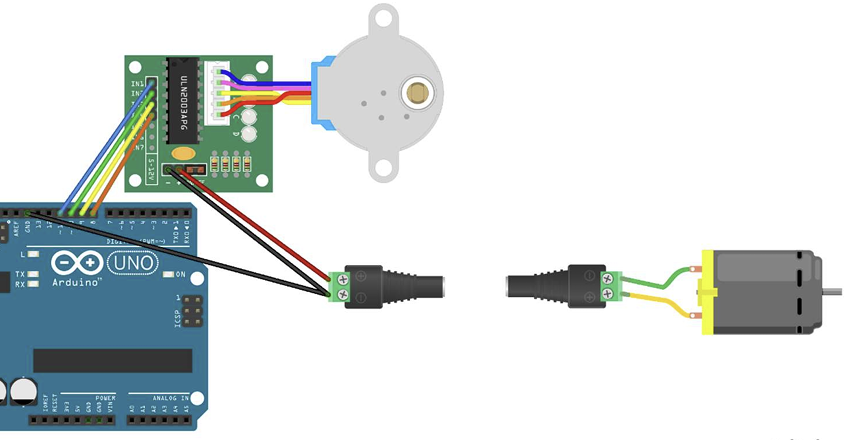
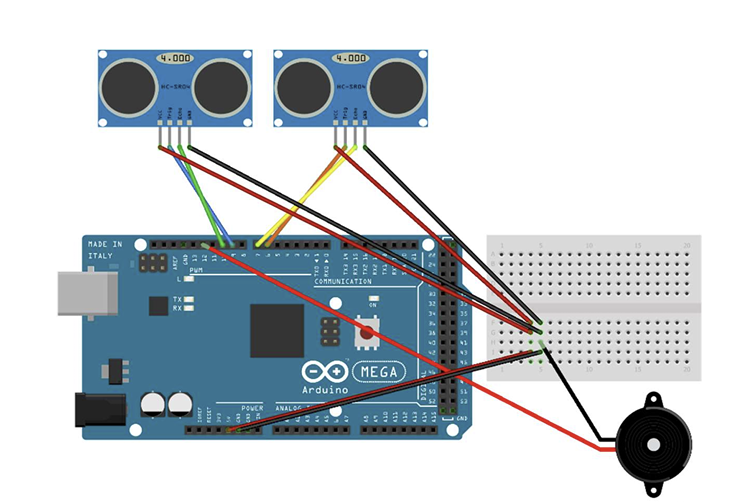
The Motorized Wooden Maze is a fast-paced 2-player game inspired by The Maze Runner, where rotating and shifting walls constantly reshape the labyrinth as players race to the center. This design project uses a stepper-driven central wall and a DC-motor crank mechanism to move vertical segments, with ultrasonic sensors detecting the winner and triggering sound effects.
Unlike static or tilt-based mazes, this Arduino-controlled design automates obstacle movement to challenge players' timing and strategy. Its precision-cut wooden construction ensures smooth gameplay and a durable, polished final build.